Do Respiratory Viruses Cause Permanent Damage?
What are viruses and how do they cause damage?
Viruses are extremely tiny, with an influenza virus being about 1/10 of a thousandth of a millimeter in diameter. It is difficult to comprehend how such a tiny little thing, that you can not even see without the aid of an electron microscope, can do so much damage.
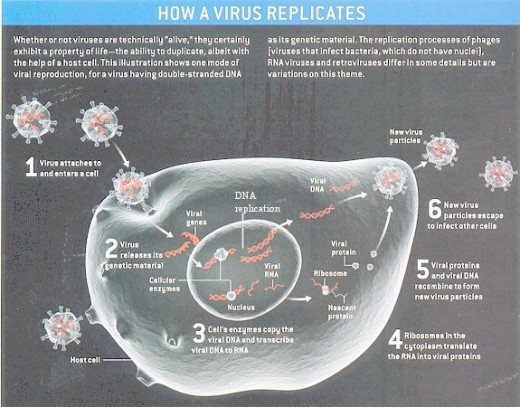
Respiratory and all other viruses have receptors on their outside surface, which "fit into" and attach to the surface of cell walls. They use these receptors to lock onto target cells, and then work their way into the cell, invading it.. Neuraminidase and hemagglutinin are proteins found on the envelope, or coat, of the virus that help the virus to lock on to and invade its target cells. Once inside the cell they utilize the inner contents of the cell to reproduce thousands or even millions of copies of newly replicated viruses, which are released and go on to infect other cells, or they are expelled from the body with every cough or sneeze, to infect new victims.
We all know that respiratory viruses are very easily transmitted through respiratory droplets released into the air by coughing or sneezing, and which we then breathe into our own respiratory systems, or by touching infected items and then touching our noses, eyes, or mouths. Respiratory viruses can live on surfaces, in some cases, for up to 72 hours!
Respiratory viruses can very easily be spread to other people. An infected person may spread germs to others by coughing, sneezing, or being in close contact with others. Viruses can be left on objects such as door knobs, counters, telephones, tables, cribs, and toys.
Viral infections trigger reactions which cause cellular and oxidative stress on DNA and many types of cells. Viruses have the capability of selectively attacking specific cell types. This predilection of viruses for certain cell types is called "tropism". Depending on the tropism of the virus, targeted cells could be respiratory tissue cells, lymphocytes, T Cells, phagocytes, or virtually any kind of cell.
Some diseases in which viral infections have been implicated as a causative factor, depending on which cells the virus has caused damage to, include: diabetes, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis and other connective tissue diseases, psoriasis, inflammatory neurologic diseases, fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue fyndrome, prostate cancer, respiratory syncitial virus disease, Aids, some lymphomas and leukemias, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, multiple sclerosis, hypertension, kidney disease, stillbirths, thyroid diseases, and even reproductive diseases. In fact, having had a viral infection has been cited as a cause of almost all autoimmune disease conditions!
In this discussion, however, we will mostly focus on respiratory tissue and heart muscle cells, which are the ones mainly affected by respiratory influenza viruses. Respiratory virus infection may result in considerable lung injury, caused by immunopathologic tissue damage.
A variety of viruses, such as the influenza viruses A and B, the human respiratory syncytial virus, the parainfluenza viruses, and the adenoviruses, cause seasonal respiratory tract infections. Respiratory viral infections can cause acute and chronic airway damage, which is attributable to the production of allo-reactive cytokines during viral replication. Current clinical data suggests that respiratory viruses play a possible role in the development of Bronchiolitis Obliterans, especially in babies or small children, and in people who have pre-existing conditions such as asthma, COPD, chronic bronchitis, pulmonary fibrosis, and in lung transplant recipients.
DISEASES THAT CAN BE CAUSED BY RESPIRATORY VIRUSES:
BRONCHIOLITIS OBLITERANS:
Bronchiolitis - An Overview
What is Bronchiolitis?
Bronchiolitis is the inflammation and thickening of the bronchioles in the lungs, which affects breathing. It can be triggered by certain (viral) infections, drug reactions, or for no obvious reason. The condition often progresses to cause serious respiratory problems, such as Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), or even death. Small babies less than 6-12 weeks old and lung transplant patients are the most susceptible to bronchiolitis, as are those with compromised immune systems, respiratory diseases, cystic fibrosis, heart disease, and those over the age of 65. In the case of the H1N1 virus, it is also known that cytokine storms are more likely in those with strong immune systems. It is precisely these cytokine storms which can cause damage to lung tissue.
The bronchioles are tiny tubes (airways) inside the lungs, which carry air to the alveoli (tiny air sacs) in the lungs. When irritation or infection is present, these small airways become inflamed and swollen, making it hard for you to breathe. The airways become filled with fluid, mucus, and dead tissue, and muscles around them tighten, making them smaller. This gives you the feeling of "drowning in fluid", and breathing becomes extremely difficult, or impossible.
Bronchiolitis is usually caused by viruses, and most often by the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). However, other viruses can also cause bronchiolitis, including those that cause influenza (the flu), colds, and pneumonia.
The term "obliterans" refers to inflammation of the bronchioles, which partially destroys (obliterates) the small airways. The term "pneumonia" refers to inflammation of the lung tissue around the bronchioles - but not due to infection with an organism. A more accurate term to describe this inflammation would be "pneumonitis" - which means inflammation - but "pneumonia" is the term that has stuck.
Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia (BOOP) is inflammation of the small airways (bronchioles) and surrounding tissue in the lung. It can affect a small segment of the lung or the entire lung. Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia isn't associated with infection or lung cancer.
Bronchiolitis is difficult to diagnose, and is often mis-diagnosed. A doctor may make a diagnosis of bronchiolitis based on:
Personal medical history
High-resolution computerized tomography (CT) scan of the lungs
Removal of lung tissue (biopsy) for examination under a microscope
Risk Factors:
Babies less than 6-12 weeks of age
Age 65 or more
Compromised immune system
Having a respiratory disease (Asthma, COPD, Chronic Bronchitis, IPF, Emphysema)
Cystic fibrosis, heart disease
Allergies
Down syndrome
Treatment:
Ventilator, oxygen, nebulizer treatments, fluids, IV fluid replacement, bronchodilators, steroids, antibiotics, antivirals, NSAIDS (tylenol, ibuprofen)
Bronchiolitis Obliterans is?
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/bronchiolitis-obliterans/an00307
GET BREATHE EASY TEA! IT WORKS!
LVD - LEFT VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION:
Common Respiratory Virus Identified As Cause Of Heart Muscle Damage That Can Lead To Sudden Death
Approximately 40 of every 100,000 Americans suffer from LVD, which costs the US economy an estimated $12 Billion a year. It is not a common disease, but it is eye-catching. LVD is one of the common causes of someone suddenly dropping dead while participating in sports.
LVD can be caused by coronary disease, genetic defect, or even tissue damage from using cocaine. But viruses, almost equally adenoviruses and enteroviruses, have been known as a causative factor of LVD in children and adults for around 50 years. Typically, after recovering from a virus, the person starts feeling bad about 3 weeks later, when the heart becomes enlarged and starts pumping poorly.
It is often difficult to diagnose the cause of LVD, and despite the research that links viruses to LVD in children, many doctors reject the idea that they can cause the same in adults.
Patients who feel poorly several weeks after a flu-like illness should contact their physicians.
Usually symptoms will be fatigue or shortness of breath that continue after recovery from the respiratory illness. A physical exam or chest X-ray can reveal heart enlargement."
For more information on the current Influenza Epidemic, please go to the CDC's H1N1 Info Page: